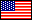
1⁄1Bell-Textron XV-3 Tiltrotor
...
Post a Comment
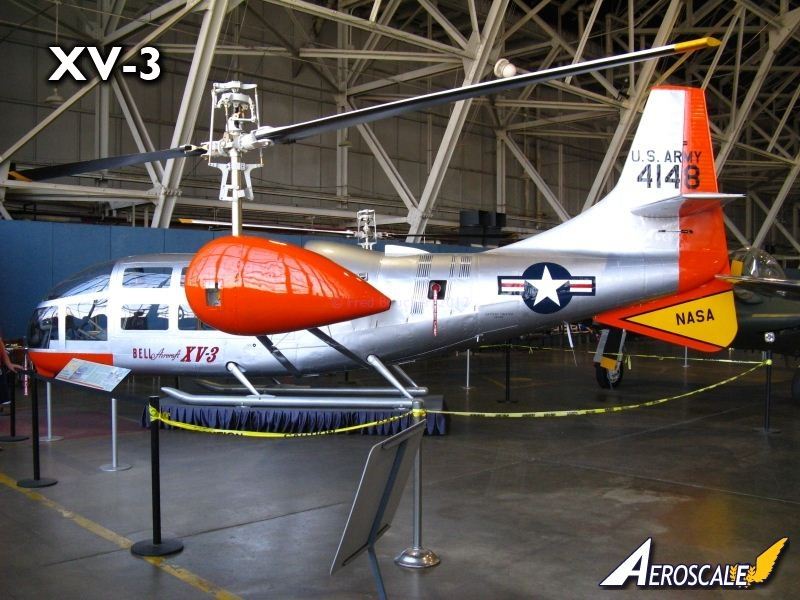
The product of a 1951 joint U.S. Air Force-U.S. Army initiative, the Bell XV-3 became the world's first successful vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) tilt-rotor aircraft. By combining the vertical takeoff and hovering capabilities of a helicopter with the speed and range of a fixed-wing aircraft, the XV-3 offered great military potential, but it never went beyond the testing phase.
Nevertheless, the XV-3 paved the way for the modern tilt-rotor CV-22 Osprey. Like a helicopter, tilt-rotor aircraft use their propellers, or proprotors, for vertical lift. When the aircraft gains enough altitude, the proprotors rotate forward for thrust, and the wings provide the lift. This configuration is more efficient for level flight and allows greater speed and range. A tilt-rotor aircraft is different from a tilt-wing aircraft, such as the Museum's Chance-Vought/LTV XC-142A, which rotates the entire wing.
Bell completed two XV-3s in 1955, and hover tests started in August 1955. The first XV-3 was damaged beyond repair, but testing continued with the second aircraft. The first complete conversion from takeoff to horizontal flight and back -- the first ever for a tilt-rotor aircraft -- took place on Dec. 19, 1958. After testing ended in 1965, the surviving XV-3 went on display at Fort Rucker, Ala., and later into storage.
In 2004 the XV-3 was moved to the Bell Helicopter Textron facility at Arlington, Texas, where a group of current and retired Bell engineers restored the aircraft. It arrived at the museum in 2007.
TECHNICAL NOTES: Engine: Pratt & Whitney R-985 Maximum speed: 184 mph Wingspan: 31 ft. 4 in. (rotor tip to rotor tip: 52 ft. 6 in.) Length: 30 ft. 4 in. Source: National Museum of the USAF. Accessed on 1 November, 2012.
Nevertheless, the XV-3 paved the way for the modern tilt-rotor CV-22 Osprey. Like a helicopter, tilt-rotor aircraft use their propellers, or proprotors, for vertical lift. When the aircraft gains enough altitude, the proprotors rotate forward for thrust, and the wings provide the lift. This configuration is more efficient for level flight and allows greater speed and range. A tilt-rotor aircraft is different from a tilt-wing aircraft, such as the Museum's Chance-Vought/LTV XC-142A, which rotates the entire wing.
Bell completed two XV-3s in 1955, and hover tests started in August 1955. The first XV-3 was damaged beyond repair, but testing continued with the second aircraft. The first complete conversion from takeoff to horizontal flight and back -- the first ever for a tilt-rotor aircraft -- took place on Dec. 19, 1958. After testing ended in 1965, the surviving XV-3 went on display at Fort Rucker, Ala., and later into storage.
In 2004 the XV-3 was moved to the Bell Helicopter Textron facility at Arlington, Texas, where a group of current and retired Bell engineers restored the aircraft. It arrived at the museum in 2007.
TECHNICAL NOTES: Engine: Pratt & Whitney R-985 Maximum speed: 184 mph Wingspan: 31 ft. 4 in. (rotor tip to rotor tip: 52 ft. 6 in.) Length: 30 ft. 4 in. Source: National Museum of the USAF. Accessed on 1 November, 2012.
Copyright ©2021 by Frederick Boucher. Images also by copyright holder unless otherwise noted. The views and opinions expressed herein are solely the views and opinions of the authors and/or contributors to this Web site and do not necessarily represent the views and/or opinions of AeroScale, KitMaker Network, or Silver Star Enterrpises. Images also by copyright holder unless otherwise noted. Opinions expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of AeroScale. All rights reserved. Originally published on: 2012-11-01 00:00:00. Unique Reads: 12783